Family planning in India seems to be a woman’s responsibility as female sterilisation remains the most popular contraceptive method among married couples, data analysed by CNN-News18 shows.
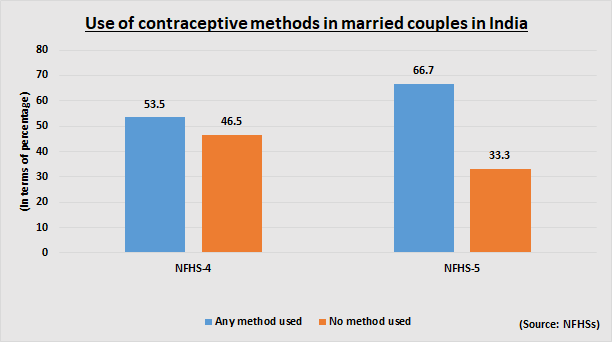
According to the National Family Health Survey-5 (NFHS) (2019-21), about 67% married couples in India are using at least one contraceptive method – it stands at 69.3% in urban areas while 65.6% for rural areas.
The current numbers are an improvement from 2015-16, when the contraceptive prevalence rate among married women was just 54%.
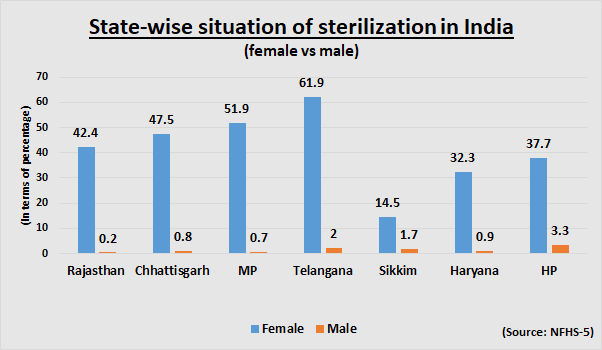
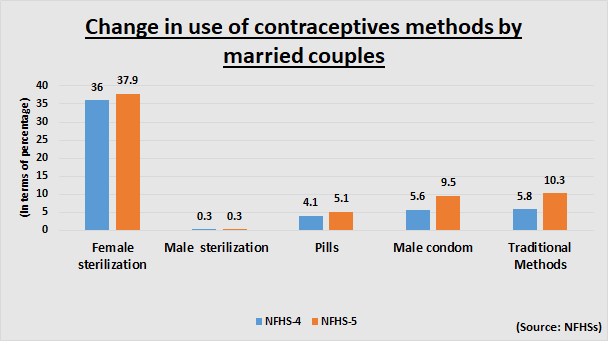
“Among currently married women aged 15-49, 38% use female sterilization, followed by male condoms (10%) and pills (5%). Ten per cent use a traditional method, mostly the rhythm method,” the NFHS-5 reads.
The numbers also show that out of those who opted for female sterilisation, only 58.7% were informed about the side effects or problems, while just 50.8% were told what they can do if they experienced any side effects. The report also shows that 65% of women were informed by a health or family planning worker about other methods that could be used.
Contraceptive methods are used to limit or space the number of children couples have. The report also suggested that the knowledge of contraceptive methods is almost universal in India, with more than 99% of married women and men knowing at least one method of contraception. It says that about 75% of women have heard or seen a family planning message in the past few months. Exposure to family planning messages is slightly higher for men at 78%.
The report shows that about 33% of married couples are not using any method. This is also an improvement from the last NFHS as about 47% couples were not using any contraceptive method during the 2015-16 survey.
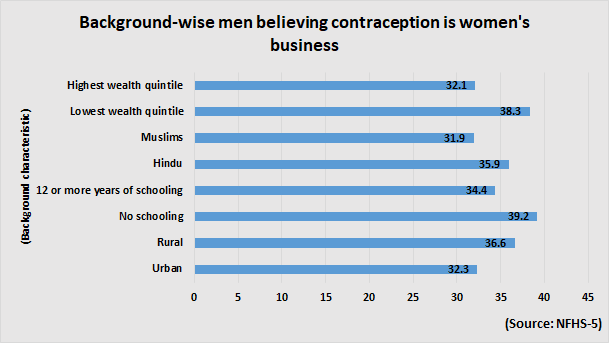
‘CONTRACEPTION IS WOMEN’S BUSINESS’
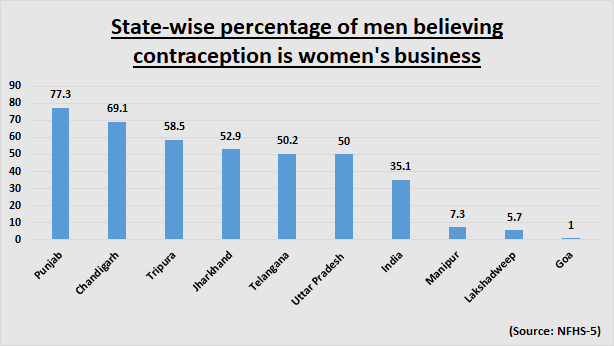
More than 35% men aged 15-54 feel that contraception is women’s business and a man should not have to worry about it, the report shows. “More than one-third of men believe that contraception is women’s business and that men should not have to worry about it,” the report added.
In Punjab, over 77% of men believe that contraception is women’s business — highest in the country. Chandigarh stood second with 69% men having similar beliefs.
The numbers further show that men across the background have similar beliefs – be it age groups, schooling levels, religion or wealth quintile, with certain exceptions. Among exceptions are young men — just 30% of men between 15 and 19 years have this opinion. The highest variation can be seen when men are divided in terms of religions — about 65% Sikh men feel that contraception is women’s business, while when it comes to Jains, the share is just 17.4% and in Buddhists, it is 21%.
The numbers further suggest that men also feel that women who use contraceptives may become promiscuous. “Twenty per cent of men believe that a woman who uses contraception may become promiscuous,” the report added.
Punjab (44%) and Chandigarh (41%) are the top regions where most men feel that women who use contraception may become promiscuous.
A Different Trend in Unmarried Couples
Among sexually active unmarried couples, male condoms are the most commonly used method (27%), followed by female sterilization (21%). The use of condoms increased from 12% in 2015-16 to 27% in 2019-21 among these couples.
STATE-WISE USE OF CONTRACEPTIVE METHODS
The total demand for family planning among currently married couples in India increased from 66% in 2015-16 to 76% in 2019-21. Further, modern contraceptive use by currently married women has increased from 48% to 56% between 2015-16 and 2019-21.
Modern methods include male and female sterilisation, injectables, intrauterine devices (IUDs/ PPIUDs), contraceptive pills, implants, female and male condoms, diaphragm, foam/jelly, the standard days method, lactational amenorrhoea method, and emergency contraception.
Across India, the use of contraceptive methods is the lowest in Meghalaya (27%), Mizoram (31%), Ladakh (51%), Lakshadweep (53%) and Bihar (56%). It is highest in Chandigarh (77%), Delhi (76%) and in West Bengal, Odisha, and Himachal Pradesh (74% each).
Read all the Latest News India and Breaking News here